Sonochemical Synthesis of Optically Tuneable Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles
- Admin

- Jan 19, 2018
- 1 min read
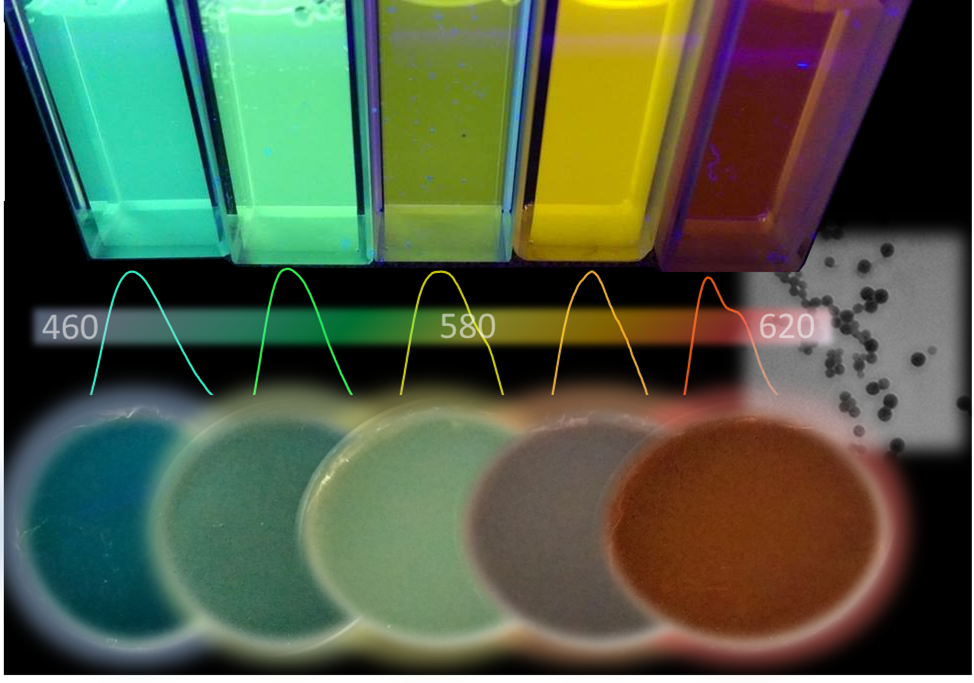
The development of novel and simple methodologies for the obtaining of semiconductive polymer nanoparticles with fine-tuned optical properties represents nowadays a challenging research area as it involves a simultaneous chemical modification and nanostructuration of the polymer. Here, starting from poly[2-methoxy-5-(2-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylenevinylene], this objective is achieved with the one-pot synthesis of oligomers with tunable conjugation length and their nanostructuration, employing a miniemulsion method. Ultrasound irradiation of heterogeneous mixtures leads to the formation of hypochlorous acid that disrupts the electronic conjugation through polymer chain cleavage. Moreover, control over the degree of the electronic conjugation of the oligomers, and therefore of the optical properties, is achieved simply by varying the polymer concentration of the initial solution. Finally, the presence of surfactants during the sonication allows for the formation of nanoparticles with progressive spectral shift of the main absorption (from λmax = 476 to 306 nm) and emission bands (from λmax = 597 to 481 nm). The integration of conducting polymer nanoparticles into polymeric matrices yields self-standing and flexible fluorescent films.
C. Bellacanzone, C. Roscini, M. C. R. Delgado, R. P. Ortiz, D. Ruiz-Molina, Part. Part. Syst. Charact.2018, 1700322. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201700322


Comments